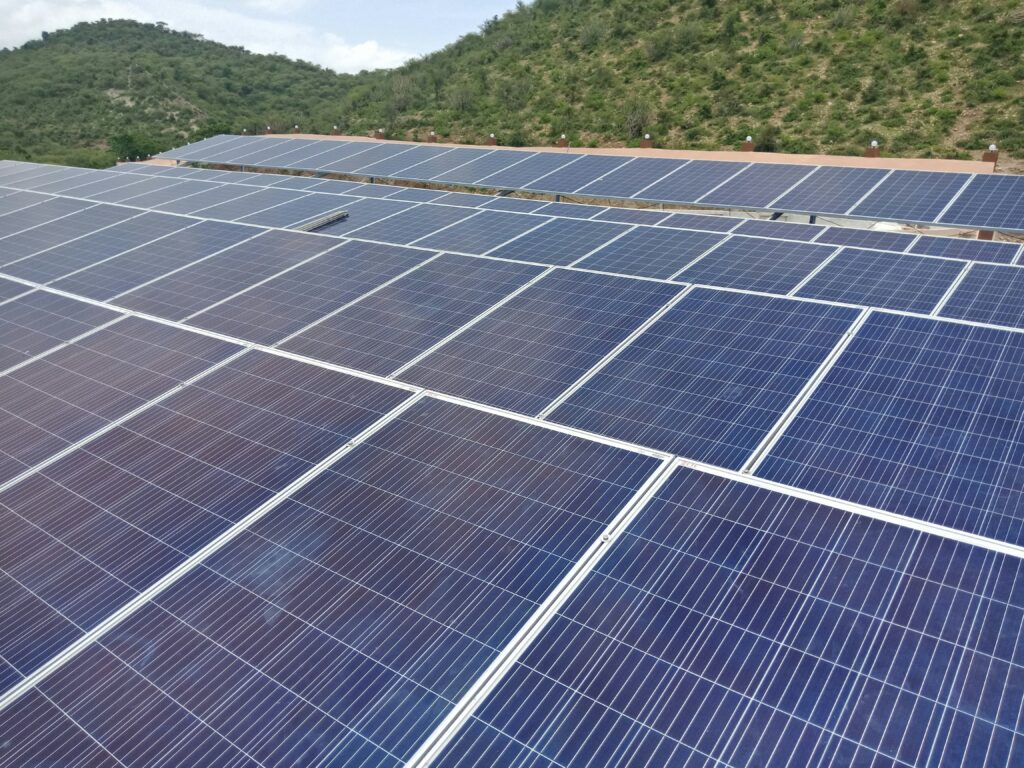

Why Solar?

- reduce electricity bill
- environment friendly
-
Government support and
promotion for the solar -
Generate, consume and
sell the surplus production -
Conservation of energy
sources like coal and gas
- zero energy dependency
- Almost zero maintenance
- Loans available
- long life
Type of solar panel
Polycrystalline
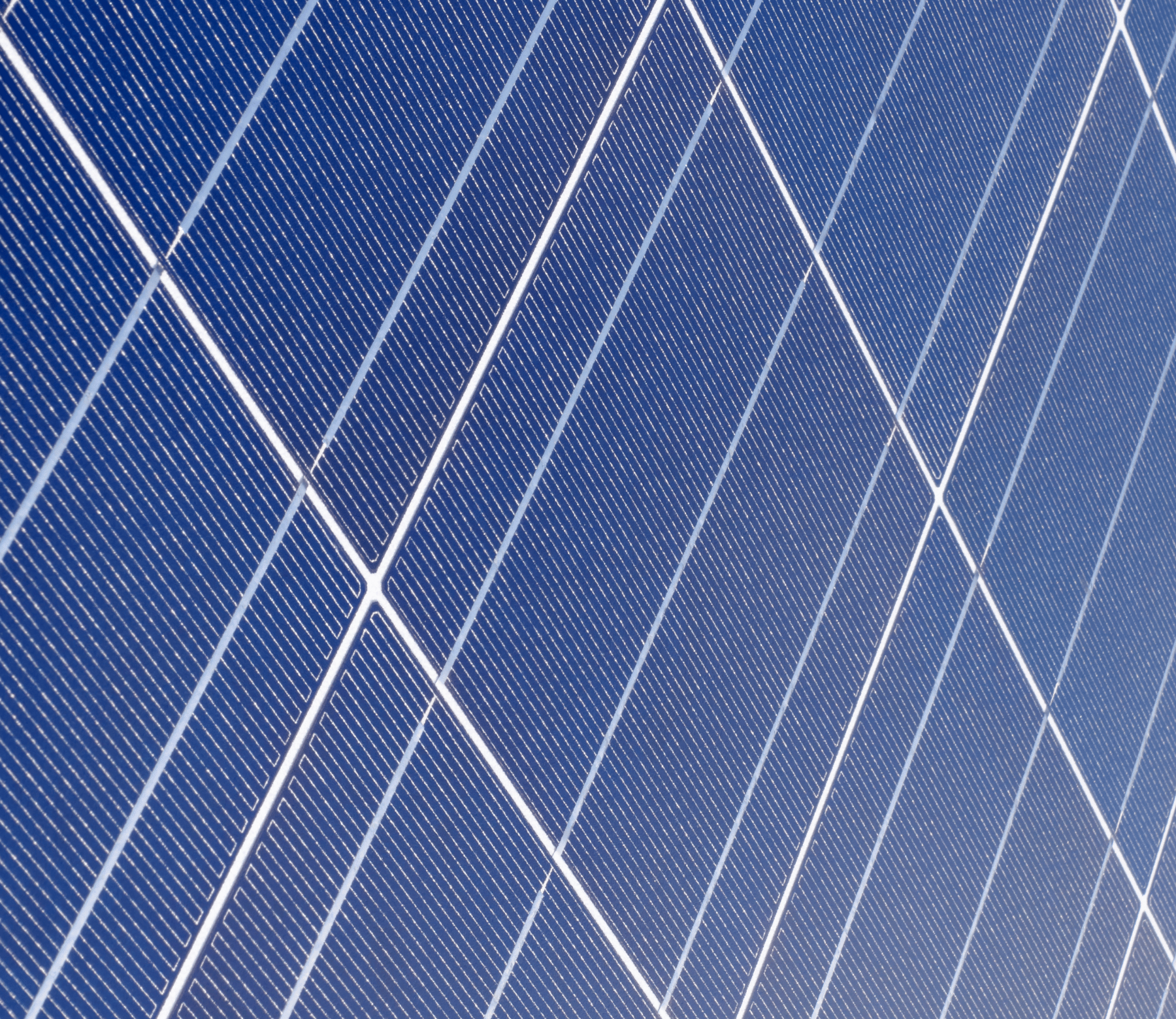
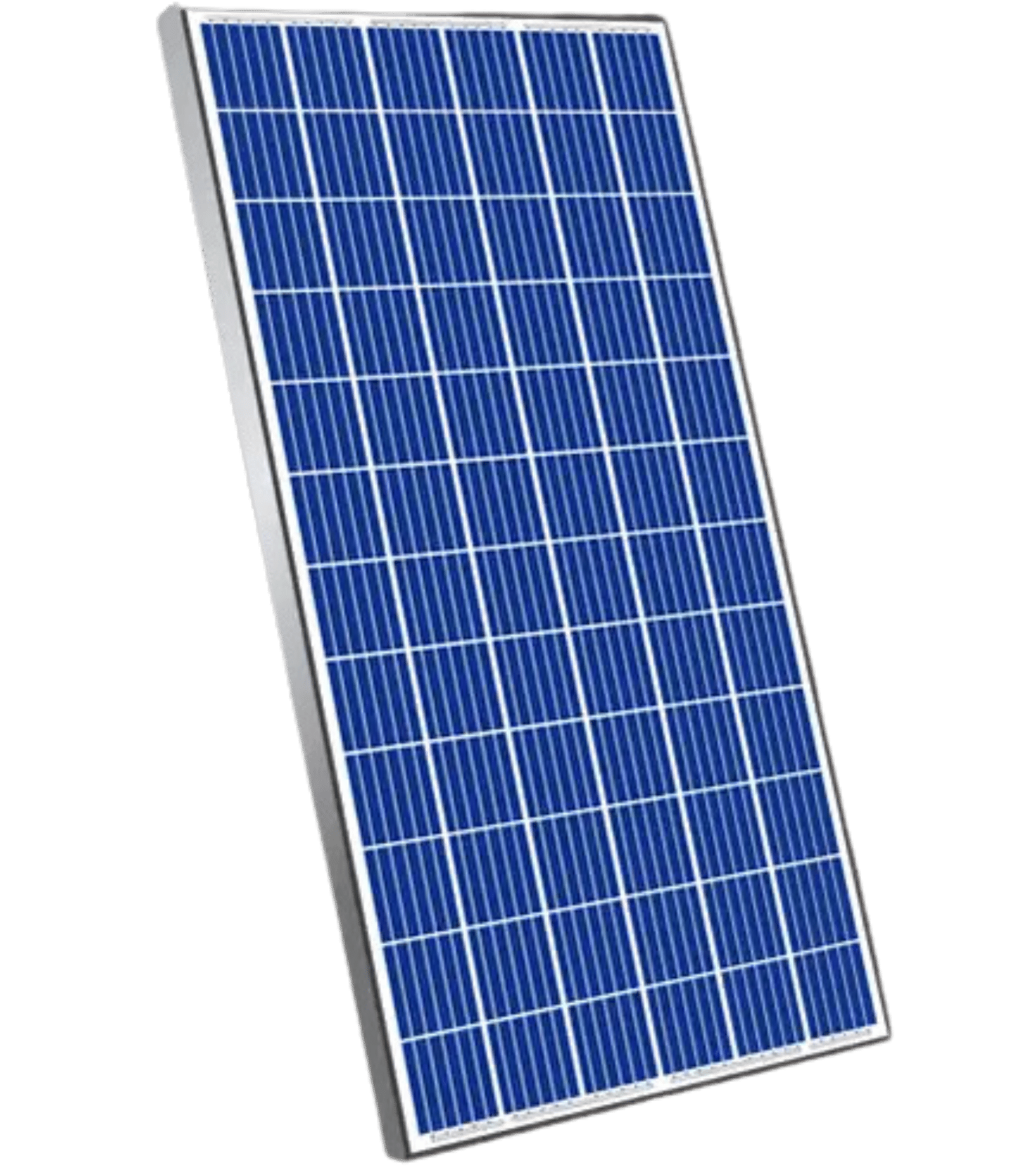


Multiple crystals are randomly arrange to convert solar power into electricity. Polycrystalline solar panels tend to have slightly lower heat tolerance than mono crystalline solar panels. This technically means that they perform slightly worse than mono crystalline solar panels in high temperatures. Heat can affect the performance of solar panels and shorten their life spans. However, this effect is minor, and most homeowners do not need to take it into account.
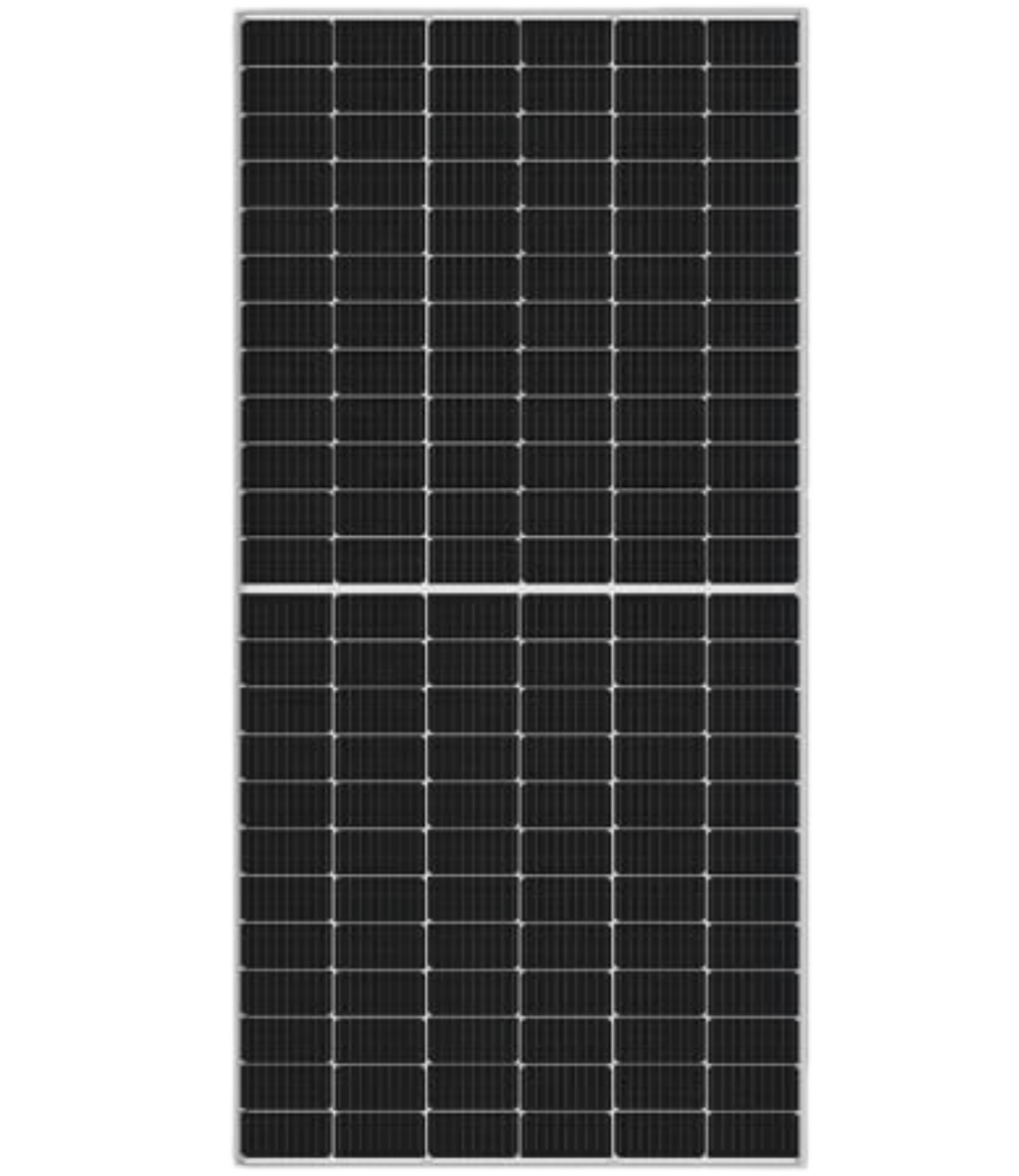


Mono Crystalline
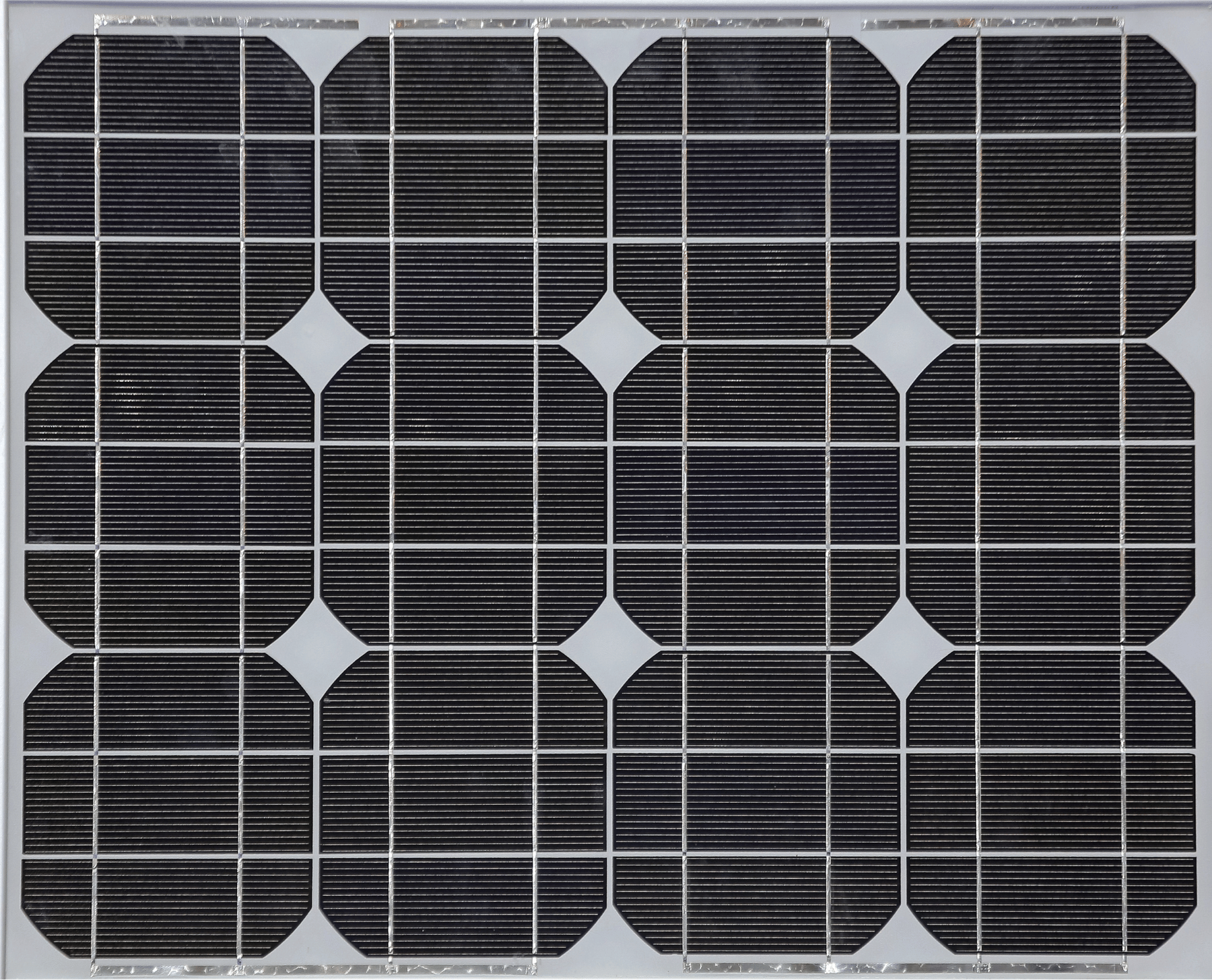

Mono crystals are randomly arrange to convert solar power into electricity. To optimize performance and lower costs of a single mono crystalline solar cell, four sides are cut out of the cylindrical ingots to make silicon wafers, which is what gives mono crystalline solar panels their characteristic look. A good way to separate mono- and polycrystalline solar panels is that polycrystalline solar cells look perfectly rectangular with no rounded edges.
Bifacial panels

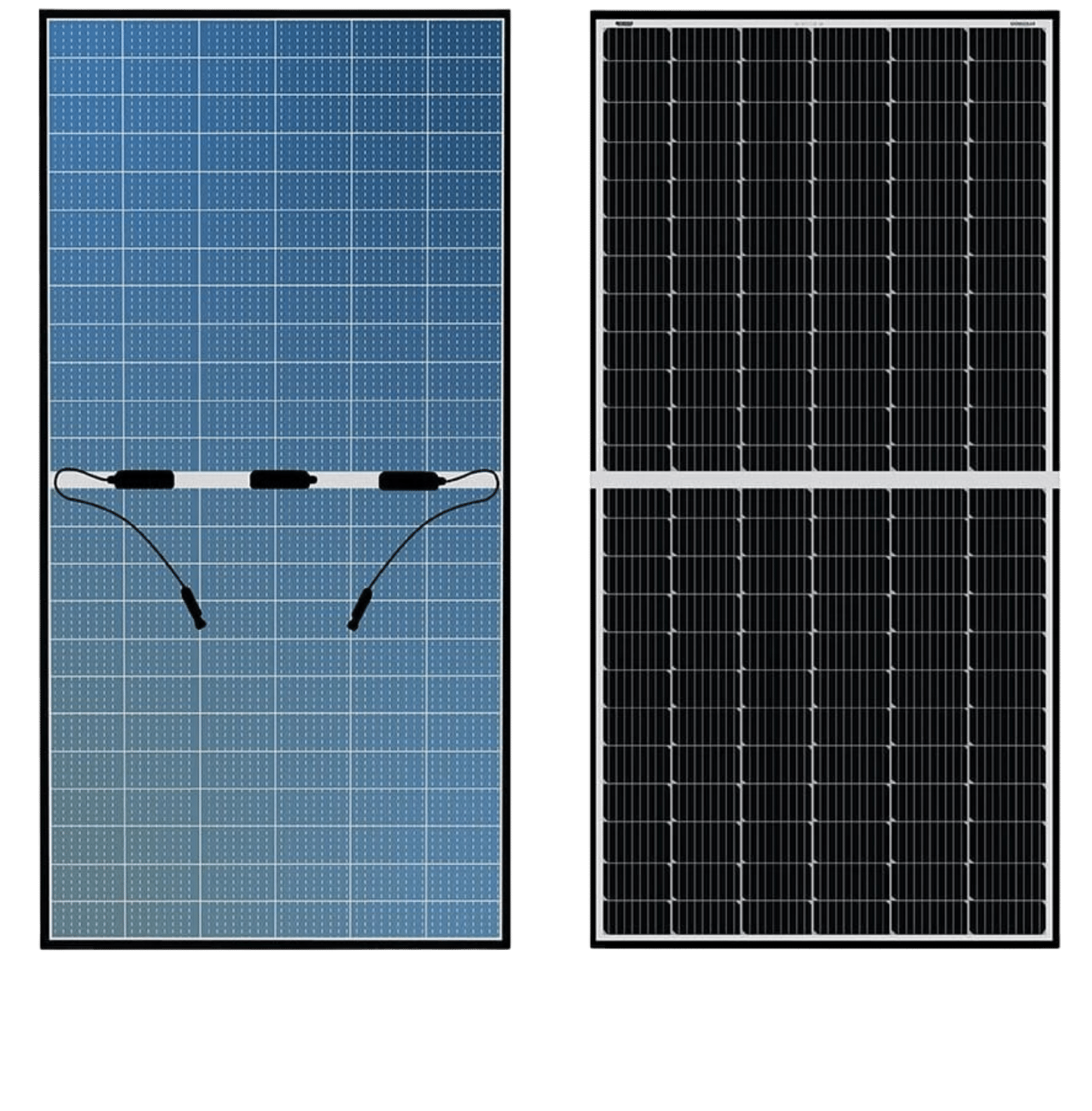
Bifacial solar modules offer many advantages over traditional solar panels. Power can be produced from both sides of a bifacial module, increasing total energy generation. They’re often more durable because both sides are UV resistant, and potential-induced degradation (PID) concerns are reduced when the bifacial module is frameless. Balance of system (BOS) costs are also reduced when more power can be generated from bifacial modules in a smaller array footprint. Some manufacturers claim that bifacial solar panels can generate up to 30% more energy than conventional monofacial solar panels.

Solar plant setup

off- grid system
The second one is the off-grid system in which the rooftop solar system is not linked to the main grid. This system can run on its own with its own battery. The solar power generated from the rooftop solar system charges the battery which is then used to power various applications. This system is very useful when there is no grid supply or when the supply is very erratic with frequent breakdowns.
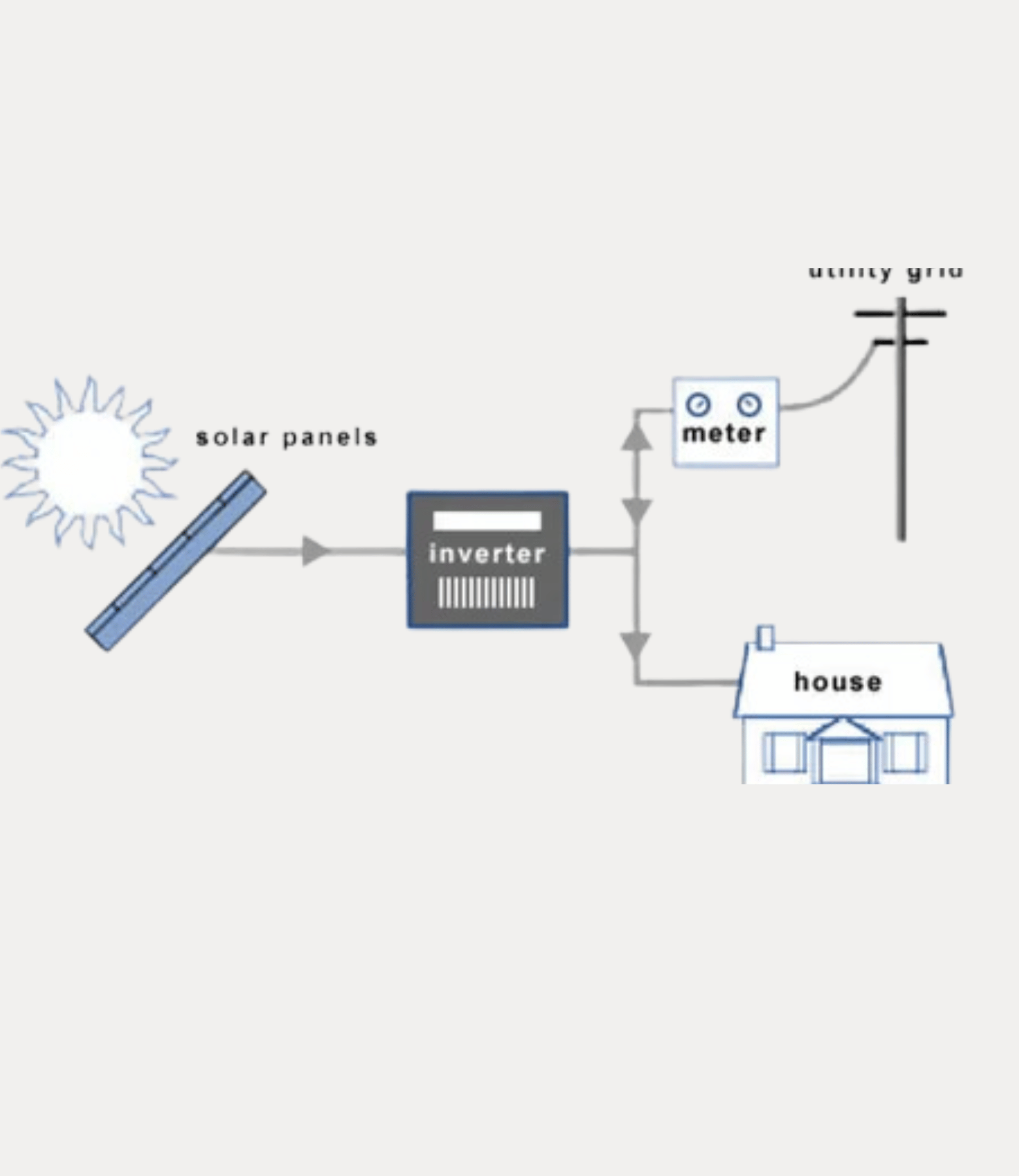
On grid system
One of them is the on-grid system in which the rooftop solar system is integrated with the main grid supply. This system allows power to be used from the grid supply only when the rooftop solar system is unable to supply the required power. Thus, a well-planned rooftop system can efficiently supply power without using grid supply saving expenses otherwise incurred on using power from the grid. In fact, this system can earn revenues as any excess power generated can be fed to the grid for which DISCOMs pay compensation using ‘net metering’.
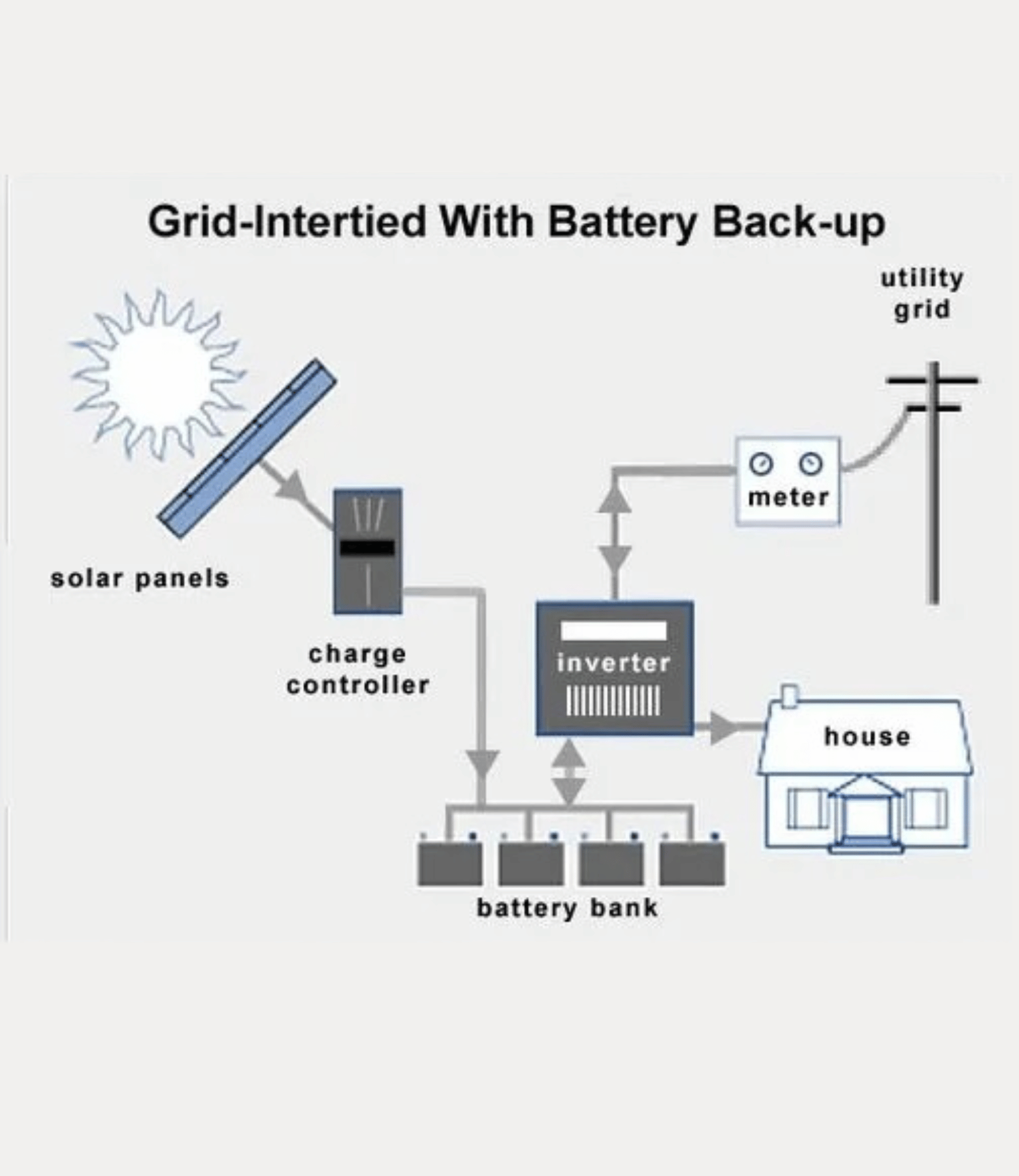
Hybrid System
The third one is the hybrid system in which both on-grid and off-grid systems work in tandem. In this type of system, though a battery is used, the advantage here is that after the battery is fully charged the excess power generated is fed to the grid which generates additional revenues for the consumer.
